Smart Mobility
CSIR Smart Mobility addresses challenges and opportunities associated with transport systems and operations, infrastructure, transport operations, and logistics management in support of industrial and sustainable development.
Impact areas
CSIR Smart Mobility impact areas focus on transport infrastructure, transport operations, and logistics management.
Transport Systems and Operations
The CSIR develops science, engineering and technology led solutions to leapfrog the performance of transport system operations in support of sustainable development. The CSIR undertakes research into:
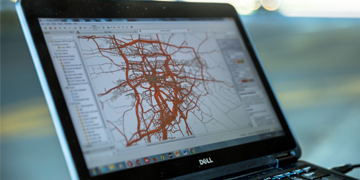
- Passenger transport, with capabilities in public transport service design, transport safety, transport network modelling and transport policy support.
- Transport infrastructure management, with capabilities in the life cycle management of transport network assets and development of associated management systems.
Transport Infrastructure Engineering
The CSIR provides research, development and implementation of practical, innovative, cost-effective and sustainable infrastructure engineering systems and technological solutions for roads, rail and ports that enable and support efficient and effective end-to-end logistics (people and goods) to enhance socio-economic development, asset preservation and industry competitiveness.
Smart Logistics Management
The CSIR adds value through its integrative and catalysing role in the national logistics landscape by providing skills, information infrastructure, and support for the adoption of integrative logistics and supply chain processes and technologies. It enhances the enabling environment within which supply chains function, and acts as an independent catalyst for improved systemic performance. It conducts independent research to enhance:
- The performance of national and regional logistics systems, as custodian and developer of information platforms and decision support capabilities; and
- Sector-level supply chain performance by acting as an independent broker in the development of end-to-end solutions, with a specific focus on the adoption of collaborative and 4IR technologies and the integration of supply chain players across resource divides.
- The fourth industrial revolution (4IR) in mobility, a newer area dedicated to accelerating the adoption and adaptation of appropriate 4IR innovations in mobility.
Strategic intent
The CSIR seeks to improve the efficiency, safety, cost and reliability of transport networks to minimise the cost of doing business and to improve quality of life. This is done through modelling, experimental designs, development of digitalisation solutions and laboratory tests. The cluster also works with other role players to contribute towards increased local content in the tools and infrastructure used along the transport value chain, such as road building materials, rail and port infrastructure and vehicles.
CSIR solutions in this domain can transform South Africa’s transport system, which is typically characterised by structural backlogs that include excessively high transport costs, and backlogs in infrastructure provision and maintenance. The digitalisation of the transport system can improve the life-cycle management of assets such as public transport vehicles, ports, railways and roadways. This is especially effective when supplemented with improved measurement of decision drivers for households, passengers, various state actors, shippers and investors.
Offerings
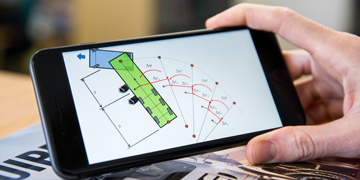
Experimental work to assist with the appropriate measurement of various mobility concepts and business models such as mobility-as-a-service, travel demand management and collaborative logistics. The CSIR is investing in a fully-fledged transport safety laboratory to help improve the management of transport safety risks. These investments are over and above the already world-class laboratories for road building materials and the physical modelling of port infrastructure.
Road, rail and port or coastal engineering to optimise the use of limited resources to support the establishment of effective, efficient and sustainable transport networks to support socio-economic development.
Development of technical capacity with partner organisations in the form of appropriate norms and standards, customised training, staff exchange programmes and dissemination of information.